Erofs-utils 中制作 EROFS 压缩镜像的代码逻辑
1. erofs-utils 是什么
erofs-utils 是一组工具,用于处理 EROFS(Enhanced Read-Only File System,增强型只读文件系统)的文件系统镜像。这包括创建、检查和解包 EROFS 镜像。EROFS 是由华为开发,主要用于 Android 和其他嵌入式系统中,特别强调高效的读取性能和对压缩数据的支持。
构建 erofs-utils 的基本过程如下:
# git clone https://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/linux/kernel/git/xiang/erofs-utils.git
# ./autogen.sh
# ./configure --prefix=$(pwd)/build --enable-lzma --enable-fuse
# make -j$(nproc)
# make install- 最后能够把对应的二进制程序都放入到
$(pwd)/build目录下
2. 制作镜像
制作镜像使用的是 erofs-utils 工具组中的 mkfs.erofs,这个工具会将一个目录树转换成一个 EROFS 镜像,该镜像可以挂载为只读文件系统。
假设我们想将 /path/to/source/dir 目录下的内容制作成 EROFS 镜像文件 /path/to/erofs.img,可以使用以下指令:
mkfs.erofs /path/to/erofs.img /path/to/source/dir这样,就能把我们在目录下的数据都压缩进 erofs 的镜像了:
[root@fedora erofs]# ./build/bin/mkfs.erofs /erofs/erofs_disk /erofs/tmp/
mkfs.erofs 1.7.1
Build completed.
------
Filesystem UUID: 92fd7f8f-9c8d-4a43-bbfa-ef3b579f551b
Filesystem total blocks: 1 (of 4096-byte blocks)
Filesystem total inodes: 2
Filesystem total metadata blocks: 1
Filesystem total deduplicated bytes (of source files): 03. 挂载镜像
挂载镜像要求 kernel 是支持 erofs 的,可以通过 lsmod | grep erofs 检查。
假设我们想将 /path/to/erofs.img EROFS 镜像文件挂载到 /path/to/mount,可以使用以下指令:
mount -t /path/to/erofs.img /path/to/mount4. 制作镜像的时候都发生了什么?
制作镜像的操作都由 mkfs.erofs 来实现,我们可以将其划分为几个不同的阶段:
- 解析命令行参数
- 扫描输入目录
- 文件压缩
- 构建文件系统元数据
- 生成镜像文件
4.1 解析命令行参数
Erofs 专门使用了一个数据结构来保存所有涉及的配置:
struct erofs_configure {
const char *c_version;
int c_dbg_lvl;
bool c_dry_run;
bool c_legacy_compress;
#ifndef NDEBUG
bool c_random_pclusterblks;
bool c_random_algorithms;
#endif
char c_timeinherit;
char c_chunkbits;
bool c_inline_data;
bool c_ztailpacking;
bool c_fragments;
bool c_all_fragments;
bool c_dedupe;
bool c_ignore_mtime;
bool c_showprogress;
bool c_extra_ea_name_prefixes;
bool c_xattr_name_filter;
bool c_ovlfs_strip;
#ifdef HAVE_LIBSELINUX
struct selabel_handle *sehnd;
#endif
/* related arguments for mkfs.erofs */
char *c_img_path;
char *c_src_path;
char *c_blobdev_path;
char *c_compress_hints_file;
char *c_compr_alg[EROFS_MAX_COMPR_CFGS];
int c_compr_level[EROFS_MAX_COMPR_CFGS];
char c_force_inodeversion;
char c_force_chunkformat;
/* < 0, xattr disabled and INT_MAX, always use inline xattrs */
int c_inline_xattr_tolerance;
u32 c_pclusterblks_max, c_pclusterblks_def, c_pclusterblks_packed;
u32 c_max_decompressed_extent_bytes;
u32 c_dict_size;
u64 c_unix_timestamp;
u32 c_uid, c_gid;
const char *mount_point;
long long c_uid_offset, c_gid_offset;
#ifdef WITH_ANDROID
char *target_out_path;
char *fs_config_file;
char *block_list_file;
#endif
/* offset when reading multi partition images */
u64 c_offset;
};在程序中将其定义为一个全局变量,在开始时,首先需要对其进行初始化:
struct erofs_configure cfg;
void erofs_init_configure(void)
{
memset(&cfg, 0, sizeof(cfg));
cfg.c_dbg_lvl = EROFS_WARN;
cfg.c_version = PACKAGE_VERSION;
cfg.c_dry_run = false;
cfg.c_ignore_mtime = false;
cfg.c_force_inodeversion = 0;
cfg.c_inline_xattr_tolerance = 2;
cfg.c_unix_timestamp = -1;
cfg.c_uid = -1;
cfg.c_gid = -1;
cfg.c_pclusterblks_max = 1;
cfg.c_pclusterblks_def = 1;
cfg.c_max_decompressed_extent_bytes = -1;
}然后把可选的配置先初始化到默认配置:
static void erofs_mkfs_default_options(void)
{
cfg.c_showprogress = true;
cfg.c_legacy_compress = false;
cfg.c_inline_data = true;
cfg.c_xattr_name_filter = true;
sbi.blkszbits = ilog2(min_t(u32, getpagesize(), EROFS_MAX_BLOCK_SIZE));
sbi.feature_incompat = EROFS_FEATURE_INCOMPAT_ZERO_PADDING;
sbi.feature_compat = EROFS_FEATURE_COMPAT_SB_CHKSUM |
EROFS_FEATURE_COMPAT_MTIME;
/* generate a default uuid first */
erofs_uuid_generate(sbi.uuid);
}值得注意的是,这里出现了一个 sbi 的变量,他代表着 erofs 的 superblock,也是定义为一个全局变量:
struct erofs_sb_info {
struct erofs_device_info *devs;
char *devname;
u64 total_blocks;
u64 primarydevice_blocks;
erofs_blk_t meta_blkaddr;
erofs_blk_t xattr_blkaddr;
u32 feature_compat;
u32 feature_incompat;
u64 build_time;
u32 build_time_nsec;
u8 extslots;
unsigned char islotbits;
unsigned char blkszbits;
/* what we really care is nid, rather than ino.. */
erofs_nid_t root_nid;
/* used for statfs, f_files - f_favail */
u64 inos;
u8 uuid[16];
char volume_name[16];
u16 available_compr_algs;
u16 lz4_max_distance;
u32 checksum;
u16 extra_devices;
union {
u16 devt_slotoff; /* used for mkfs */
u16 device_id_mask; /* used for others */
};
erofs_nid_t packed_nid;
u32 xattr_prefix_start;
u8 xattr_prefix_count;
struct erofs_xattr_prefix_item *xattr_prefixes;
int devfd, devblksz;
u64 devsz;
dev_t dev;
unsigned int nblobs;
unsigned int blobfd[256];
struct list_head list;
u64 saved_by_deduplication;
};接下来就是解析命令行参数了,这里把所有的逻辑都写到 mkfs_parse_options_cfg 里面了,有种力大飞转的美感 : (
static int mkfs_parse_options_cfg(int argc, char *argv[])
{
char *endptr;
int opt, i, err;
bool quiet = false;
while ((opt = getopt_long(argc, argv, "C:E:L:T:U:b:d:x:z:",
long_options, NULL)) != -1) {
switch (opt) {
case 'z':
i = mkfs_parse_compress_algs(optarg);
if (i)
return i;
break;
...
default: /* '?' */
return -EINVAL;
}
}
...
return 0;
}为了更好地理解这一坨代码在解析什么,我们可以先看一下 mkfs.erofs 的 help 文档:
[root@0f5ed24efcd4 erofs]# ./build/bin/mkfs.erofs --help
usage: [options] FILE SOURCE(s)
Generate EROFS image (FILE) from DIRECTORY, TARBALL and/or EROFS images. And [options] are:
-b# set block size to # (# = page size by default)
-d# set output message level to # (maximum 9)
-x# set xattr tolerance to # (< 0, disable xattrs; default 2)
-zX[,Y][:..] X=compressor (Y=compression level, optional)
alternative algorithms can be separated by colons(:)
-C# specify the size of compress physical cluster in bytes
-EX[,...] X=extended options
-L volume-label set the volume label (maximum 16)
-T# set a fixed UNIX timestamp # to all files
-UX use a given filesystem UUID
--all-root make all files owned by root
--blobdev=X specify an extra device X to store chunked data
--chunksize=# generate chunk-based files with #-byte chunks
--compress-hints=X specify a file to configure per-file compression strategy
--exclude-path=X avoid including file X (X = exact literal path)
--exclude-regex=X avoid including files that match X (X = regular expression)
--force-uid=# set all file uids to # (# = UID)
--force-gid=# set all file gids to # (# = GID)
--uid-offset=# add offset # to all file uids (# = id offset)
--gid-offset=# add offset # to all file gids (# = id offset)
--gzip try to filter the tarball stream through gzip
--help display this help and exit
--ignore-mtime use build time instead of strict per-file modification time
--max-extent-bytes=# set maximum decompressed extent size # in bytes
--preserve-mtime keep per-file modification time strictly
--aufs replace aufs special files with overlayfs metadata
--tar=[fi] generate an image from tarball(s)
--ovlfs-strip=[01] strip overlayfs metadata in the target image (e.g. whiteouts)
--quiet quiet execution (do not write anything to standard output.)
--xattr-prefix=X X=extra xattr name prefix
--mount-point=X X=prefix of target fs path (default: /)
Available compressors are: lzma, deflate可以看到,mkfs.erofs 的使用形式是:
mkfs.erofs [OPTS] FILE SOURCE(S)
基本上,这里的每一个可配置的参数会被映射到程序的数据结构中,解析这一系列的参数使用的是 getopt_long,这是一个 GNU getopt 函数的扩展,getopt 是 POSIX 标准的一部分。使用时,getopt_long 会逐步解析每一个参数,然后将其转化为对应的返回值。getopt_long 会接受一个短参数(字符串形式)和长参数(结构体形式),并返回匹配到的参数的短参数值(匹配到对应的短参数或长参数指定的短参数形式)。短参数的每个字符代表一个短选项,如果选项需要参数,则在该字符后面加上冒号。
mkfs.erofs 的长参数定义如下:
// long_options
static struct option long_options[] = {
{"help", no_argument, 0, 1},
{"exclude-path", required_argument, NULL, 2},
{"exclude-regex", required_argument, NULL, 3},
#ifdef HAVE_LIBSELINUX
{"file-contexts", required_argument, NULL, 4},
#endif
{"force-uid", required_argument, NULL, 5},
{"force-gid", required_argument, NULL, 6},
{"all-root", no_argument, NULL, 7},
#ifndef NDEBUG
{"random-pclusterblks", no_argument, NULL, 8},
{"random-algorithms", no_argument, NULL, 18},
#endif
{"max-extent-bytes", required_argument, NULL, 9},
{"compress-hints", required_argument, NULL, 10},
{"chunksize", required_argument, NULL, 11},
{"quiet", no_argument, 0, 12},
{"blobdev", required_argument, NULL, 13},
{"ignore-mtime", no_argument, NULL, 14},
{"preserve-mtime", no_argument, NULL, 15},
{"uid-offset", required_argument, NULL, 16},
{"gid-offset", required_argument, NULL, 17},
{"tar", optional_argument, NULL, 20},
{"aufs", no_argument, NULL, 21},
{"mount-point", required_argument, NULL, 512},
{"xattr-prefix", required_argument, NULL, 19},
#ifdef WITH_ANDROID
{"product-out", required_argument, NULL, 513},
{"fs-config-file", required_argument, NULL, 514},
{"block-list-file", required_argument, NULL, 515},
#endif
{"ovlfs-strip", optional_argument, NULL, 516},
#ifdef HAVE_ZLIB
{"gzip", no_argument, NULL, 517},
#endif
{0, 0, 0, 0},
};根据这样的定义进行解析:
// parse
while ((opt = getopt_long(argc, argv, "C:E:L:T:U:b:d:x:z:",
long_options, NULL)) != -1) { ... }注意
这里的长参数和短参数是完全分开的,也就是说各自表达不同的含义,具体可以结合上述的手册比对。
在解析完一系列的参数之后,读取传入的 FILE 和 SOURCE(S):
// 解析 FILE
cfg.c_img_path = strdup(argv[optind++]);
if (!cfg.c_img_path)
return -ENOMEM;
// 解析 SOURCES
cfg.c_src_path = realpath(argv[optind++], NULL);
if (!cfg.c_src_path) {
erofs_err("failed to parse source directory: %s",
erofs_strerror(-errno));
return -ENOENT;
}可重复构建
除了解析一般的命令行参数之外,
erofs-utils还会检查SOURCE_DATE_EPOCH,以确保构建产物的时间戳是一致的。在构建产物中嵌入相同的时间戳是为了实现可重复构建(reproducible builds),这是一种确保软件构建过程可靠性和安全性的重要实践。
4.2 扫描输入目录
接下来,mkfs.erofs 会扫描传入的 FILE 文件路径,这在函数 dev_open 中实现:
// 打开 FILE
fd = open(dev, O_RDWR | O_CREAT | O_BINARY, 0644);
// 获取文件或设备的元数据
ret = fstat(fd, &st);
// 根据文件类型处理
switch (st.st_mode & S_IFMT) {
// 如果是块设备
case S_IFBLK:
ret = dev_get_blkdev_size(fd, &sbi->devsz);
// 如果是普通文件
case S_IFREG:
... // 处理ext4和btrfs的特殊情况
ret = ftruncate(fd, 0);
...
// 设置块大小
sbi->devsz = INT64_MAX;
sbi->devblksz = st.st_blksize;4.3 压缩文件
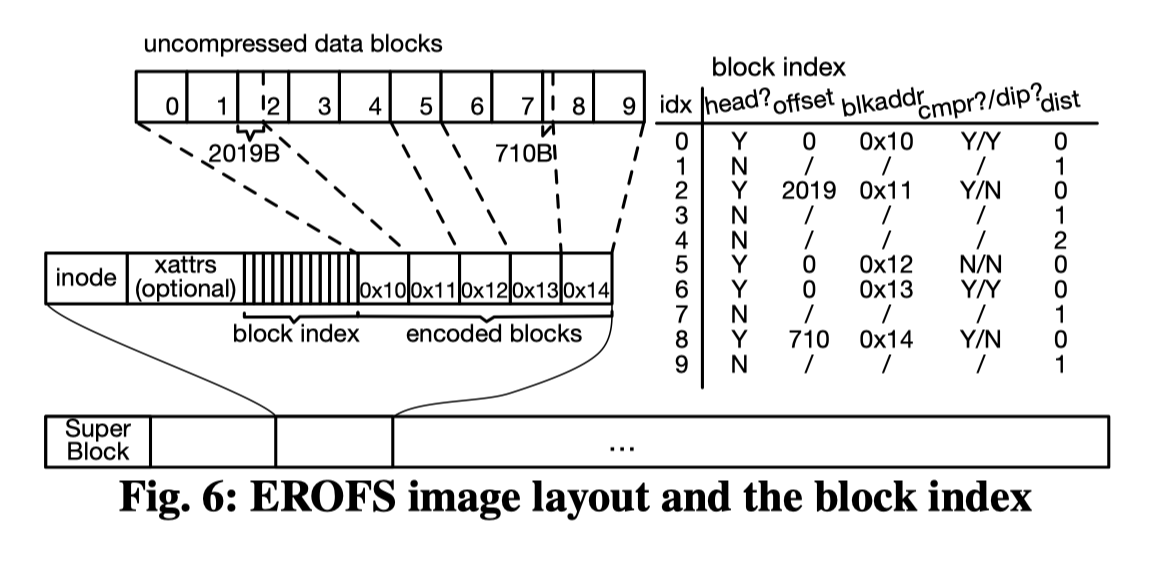
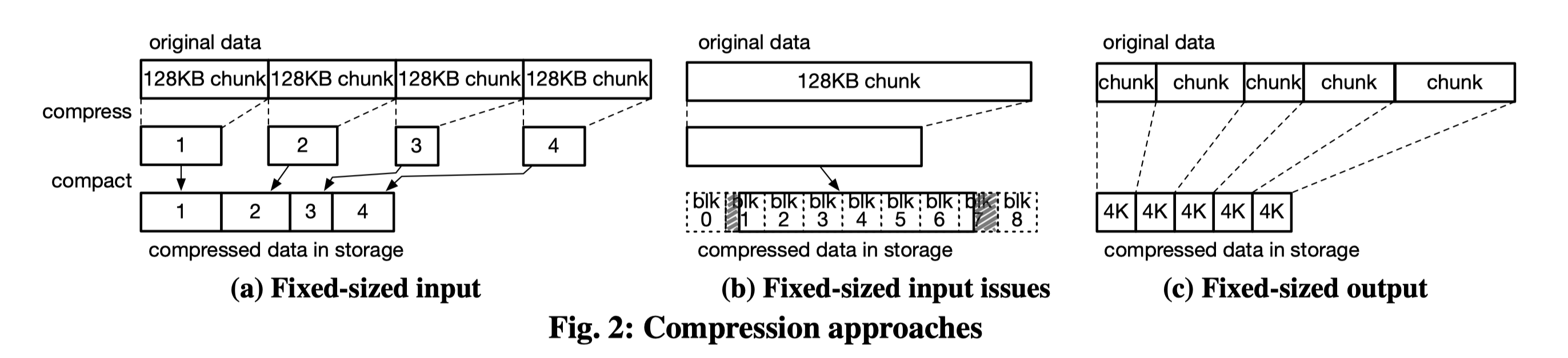
首先解释一下 erofs 的布局。erofs 采用的是 fixed-sized output compression,简而言之就是压缩的时候,原数据从头开始压缩,直到压缩得到的数据填满 4 K(即压缩时的单位大小,可配置),填满后再从新的原数据头开始压缩,周而复始得到一系列的 4 K 压缩数据和末尾的数据。
与之相对应的是 fixed-sized output compression,即每次取固定大小的数据做压缩,压缩出的数据大小不固定。如下图所示:
在 mkfs.erofs 中,需要先初始化出一系列的 bucket 来放置这些数据:
/* The maximum block size which erofs-utils supports */
#define EROFS_MAX_BLOCK_SIZE 4096
/* buckets for all mapped buffer blocks to boost up allocation */
static struct list_head mapped_buckets[META + 1][EROFS_MAX_BLOCK_SIZE];
/* return buffer_head of erofs super block (with size 0) */
struct erofs_buffer_head *erofs_buffer_init(void)
{
int i, j;
struct erofs_buffer_head *bh = erofs_balloc(META, 0, 0, 0);
if (IS_ERR(bh))
return bh;
bh->op = &erofs_skip_write_bhops;
for (i = 0; i < ARRAY_SIZE(mapped_buckets); i++)
for (j = 0; j < ARRAY_SIZE(mapped_buckets[0]); j++)
init_list_head(&mapped_buckets[i][j]);
return bh;
}
// 为 superblock 扩充空间
err = erofs_bh_balloon(sb_bh, EROFS_SUPER_END);
int erofs_bh_balloon(struct erofs_buffer_head *bh, erofs_off_t incr)
{
struct erofs_buffer_block *const bb = bh->block;
/* should be the tail bh in the corresponding buffer block */
if (bh->list.next != &bb->buffers.list)
return -EINVAL;
return __erofs_battach(bb, NULL, incr, 1, 0, false);
}
/* return occupied bytes in specific buffer block if succeed */
static int __erofs_battach(struct erofs_buffer_block *bb,
struct erofs_buffer_head *bh,
erofs_off_t incr,
unsigned int alignsize,
unsigned int extrasize,
bool dryrun)
{
const unsigned int blksiz = erofs_blksiz(&sbi);
const unsigned int blkmask = blksiz - 1;
const erofs_off_t alignedoffset = roundup(bb->buffers.off, alignsize);
const int oob = cmpsgn(roundup(((bb->buffers.off - 1) & blkmask) + 1,
alignsize) + incr + extrasize, blksiz);
bool tailupdate = false;
erofs_blk_t blkaddr;
if (oob >= 0) {
/* the next buffer block should be NULL_ADDR all the time */
if (oob && list_next_entry(bb, list)->blkaddr != NULL_ADDR)
return -EINVAL;
blkaddr = bb->blkaddr;
if (blkaddr != NULL_ADDR) {
tailupdate = (tail_blkaddr == blkaddr +
DIV_ROUND_UP(bb->buffers.off, blksiz));
if (oob && !tailupdate)
return -EINVAL;
}
}
if (!dryrun) {
if (bh) {
bh->off = alignedoffset;
bh->block = bb;
list_add_tail(&bh->list, &bb->buffers.list);
}
bb->buffers.off = alignedoffset + incr;
/* need to update the tail_blkaddr */
if (tailupdate)
tail_blkaddr = blkaddr +
DIV_ROUND_UP(bb->buffers.off, blksiz);
erofs_bupdate_mapped(bb);
}
return ((alignedoffset + incr - 1) & blkmask) + 1;
}接着,先写入 superblock:
/* make sure that the super block should be the very first blocks */
(void)erofs_mapbh(sb_bh->block);
if (erofs_btell(sb_bh, false) != 0) {
erofs_err("failed to reserve erofs_super_block");
goto exit;
}
erofs_blk_t erofs_mapbh(struct erofs_buffer_block *bb)
{
struct erofs_buffer_block *t = last_mapped_block;
if (bb && bb->blkaddr != NULL_ADDR)
return bb->blkaddr;
do {
t = list_next_entry(t, list);
if (t == &blkh)
break;
DBG_BUGON(t->blkaddr != NULL_ADDR);
(void)__erofs_mapbh(t);
} while (t != bb);
return tail_blkaddr;
}
static erofs_blk_t __erofs_mapbh(struct erofs_buffer_block *bb)
{
erofs_blk_t blkaddr;
if (bb->blkaddr == NULL_ADDR) {
bb->blkaddr = tail_blkaddr;
last_mapped_block = bb;
erofs_bupdate_mapped(bb);
}
blkaddr = bb->blkaddr + BLK_ROUND_UP(&sbi, bb->buffers.off);
if (blkaddr > tail_blkaddr)
tail_blkaddr = blkaddr;
return blkaddr;
}
static void erofs_bupdate_mapped(struct erofs_buffer_block *bb)
{
struct list_head *bkt;
if (bb->blkaddr == NULL_ADDR)
return;
bkt = mapped_buckets[bb->type] +
(bb->buffers.off & (erofs_blksiz(&sbi) - 1));
list_del(&bb->mapped_list);
list_add_tail(&bb->mapped_list, bkt);
}完成 superblock 的写入之后,开始提取压缩的一些配置:
err = erofs_load_compress_hints(&sbi);
if (err) {
erofs_err("failed to load compress hints %s",
cfg.c_compress_hints_file);
goto exit;
}erofs_load_compress_hints 函数用于从配置文件中加载压缩提示(compress hints)信息,这些信息用于指导 EROFS(Enhanced Read-Only File System)文件系统如何处理特定文件或文件模式的压缩。函数通过解析一个给定的文件来设置压缩配置,这些配置可以指定哪些文件应该被压缩以及使用什么算法进行压缩。
下一步就是初始化 compressor 了,后续压缩都是调用 compressor 的 compress_destsize 方法实现的。
// struct 关系图
erofs_compress
-> erofs_algorithm
-> erofs_compressor
// operator + compress_level
struct erofs_compressor {
int default_level;
int best_level;
int (*init)(struct erofs_compress *c);
int (*exit)(struct erofs_compress *c);
int (*setlevel)(struct erofs_compress *c, int compression_level);
int (*compress_destsize)(const struct erofs_compress *c,
const void *src, unsigned int *srcsize,
void *dst, unsigned int dstsize);
};
// 支持的压缩算法,编译的时候使用--enable_lama可以开启lzma支持,其他同理
static const struct erofs_algorithm {
char *name;
const struct erofs_compressor *c;
unsigned int id;
/* its name won't be shown as a supported algorithm */
bool optimisor;
} erofs_algs[] = {
{ "lz4",
#if LZ4_ENABLED
&erofs_compressor_lz4,
#else
NULL,
#endif
Z_EROFS_COMPRESSION_LZ4, false },
#if LZ4HC_ENABLED
{ "lz4hc", &erofs_compressor_lz4hc,
Z_EROFS_COMPRESSION_LZ4, true },
#endif
{ "lzma",
#if HAVE_LIBLZMA
&erofs_compressor_lzma,
#else
NULL,
#endif
Z_EROFS_COMPRESSION_LZMA, false },
{ "deflate", &erofs_compressor_deflate,
Z_EROFS_COMPRESSION_DEFLATE, false },
#if HAVE_LIBDEFLATE
{ "libdeflate", &erofs_compressor_libdeflate,
Z_EROFS_COMPRESSION_DEFLATE, true },
#endif
};
const struct erofs_compressor erofs_compressor_lzma = {
.default_level = LZMA_PRESET_DEFAULT,
.best_level = 109,
.init = erofs_compressor_liblzma_init,
.exit = erofs_compressor_liblzma_exit,
.setlevel = erofs_compressor_liblzma_setlevel,
.compress_destsize = erofs_liblzma_compress_destsize,
};
int z_erofs_compress_init(struct erofs_sb_info *sbi, struct erofs_buffer_head *sb_bh)
{
int i, ret;
for (i = 0; cfg.c_compr_alg[i]; ++i) {
struct erofs_compress *c = &erofs_ccfg[i].handle;
ret = erofs_compressor_init(sbi, c, cfg.c_compr_alg[i]);
if (ret)
return ret;
ret = erofs_compressor_setlevel(c, cfg.c_compr_level[i]);
if (ret)
return ret;
erofs_ccfg[i].algorithmtype =
z_erofs_get_compress_algorithm_id(c);
erofs_ccfg[i].enable = true;
sbi->available_compr_algs |= 1 << erofs_ccfg[i].algorithmtype;
if (erofs_ccfg[i].algorithmtype != Z_EROFS_COMPRESSION_LZ4)
erofs_sb_set_compr_cfgs(sbi);
}
...
return 0;
}最后,如果有去重的需求,会调用 z_erofs_dedupe_init 做初始化:
if (cfg.c_dedupe) {
if (!cfg.c_compr_alg[0]) {
erofs_err("Compression is not enabled. Turn on chunk-based data deduplication instead.");
cfg.c_chunkbits = sbi.blkszbits;
} else {
err = z_erofs_dedupe_init(erofs_blksiz(&sbi));
if (err) {
erofs_err("failed to initialize deduplication: %s",
erofs_strerror(err));
goto exit;
}
}
}4.4 构建文件系统
构建文件系统分为两步:
- 构建 xattrs:这是一些扩展属性,在这里就不过多介绍
- 构建文件系统:主要是构建以镜像目录为根的 inode 树
err = erofs_build_shared_xattrs_from_path(&sbi, cfg.c_src_path);
if (err) {
erofs_err("failed to build shared xattrs: %s",
erofs_strerror(err));
goto exit;
}
if (cfg.c_extra_ea_name_prefixes)
erofs_xattr_write_name_prefixes(&sbi, packedfile);
root_inode = erofs_mkfs_build_tree_from_path(cfg.c_src_path);
if (IS_ERR(root_inode)) {
err = PTR_ERR(root_inode);
goto exit;
}这里的 erofs_mkfs_build_tree_from_path 是最核心的部分,他将 source 文件夹下的文件构造成一颗树,并在后续进行压缩,最终写入镜像。
struct erofs_inode *erofs_mkfs_build_tree_from_path(const char *path)
{
LIST_HEAD(dirs);
struct erofs_inode *inode, *root, *dumpdir;
// 获得root的inode
root = erofs_iget_from_path(path, true);
if (IS_ERR(root))
return root;
(void)erofs_igrab(root);
root->i_parent = root; /* rootdir mark */
list_add(&root->i_subdirs, &dirs);
do {
int err;
char *trimmed;
inode = list_first_entry(&dirs, struct erofs_inode, i_subdirs);
list_del(&inode->i_subdirs);
init_list_head(&inode->i_subdirs);
// 构造文件树
err = erofs_mkfs_build_tree(inode, &dirs);
if (err) {
root = ERR_PTR(err);
break;
}
if (S_ISDIR(inode->i_mode)) {
inode->next_dirwrite = dumpdir;
dumpdir = inode;
} else {
erofs_iput(inode);
}
} while (!list_empty(&dirs));
// ...
return root;
}- 通过
erofs_iget_from_path为传入的目录文件创建目录文件 inode。该目录文件对应的是 erofs 文件系统的根目录/ - 将该 inode 的 parent 指向自己,说明自己是根目录
- 调用
erofs_mkfs_build_tree递归地为根目录创建子目录及文件,并一一对应当前目录下的子目录和文件
具体来说,在执行 erofs_iget_from_path 的过程中,有如下流程:
- 通过
lstat解析 path,可以快速获知当前 path 是目录还是文件 - 传入的是目录,因此不会执行
erofs_iget而直接调用erofs_new_inode创建一个新的 inode - 通过
erofs_fill_inode对新 inode 进行初始化
/* get the inode from the (source) path */
static struct erofs_inode *erofs_iget_from_path(const char *path, bool is_src)
{
struct stat st;
struct erofs_inode *inode;
int ret;
/* currently, only source path is supported */
if (!is_src)
return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL);
ret = lstat(path, &st);
if (ret)
return ERR_PTR(-errno);
/*
* lookup in hash table first, if it already exists we have a
* hard-link, just return it. Also don't lookup for directories
* since hard-link directory isn't allowed.
*/
if (!S_ISDIR(st.st_mode)) {
inode = erofs_iget(st.st_dev, st.st_ino);
if (inode)
return inode;
}
/* cannot find in the inode cache */
inode = erofs_new_inode();
if (IS_ERR(inode))
return inode;
ret = erofs_fill_inode(inode, &st, path);
if (ret) {
erofs_iput(inode);
return ERR_PTR(ret);
}
return inode;
}在 erofs_fill_inode 中,主要就是装填 inode 的属性。此时,也将 path 设入 inode 的 srcpath 中,建立了源文件系统与目标文件系统的映射关系。
最后,由于是新的 inode 。需要将其插入 inode_hashtable 中,用来加速查询。
static int erofs_fill_inode(struct erofs_inode *inode, struct stat *st,
const char *path)
{
int err = __erofs_fill_inode(inode, st, path);
if (err)
return err;
inode->i_mode = st->st_mode;
inode->i_nlink = 1; /* fix up later if needed */
switch (inode->i_mode & S_IFMT) {
case S_IFCHR:
case S_IFBLK:
case S_IFIFO:
case S_IFSOCK:
inode->u.i_rdev = erofs_new_encode_dev(st->st_rdev);
case S_IFDIR:
inode->i_size = 0;
break;
case S_IFREG:
case S_IFLNK:
inode->i_size = st->st_size;
break;
default:
return -EINVAL;
}
// 把inode的srcpath设置成path
inode->i_srcpath = strdup(path);
if (!inode->i_srcpath)
return -ENOMEM;
if (!S_ISDIR(inode->i_mode)) {
inode->dev = st->st_dev;
inode->i_ino[1] = st->st_ino;
}
...
erofs_insert_ihash(inode, st->st_dev, st->st_ino);
return 0;
}完成之后,进入到 erofs_mkfs_build_tree 函数,这个函数负责初始化 root 目录下的目录项,然后递归地向下进行构建。遍历时有两种情况:
- 如果遍历到文件,就调用
erofs_write_file写入 - 如果遍历到路径,递归地创建下面目录的 inode 树,也是调用
erofs_mkfs_build_tree_from_path来实现
static int erofs_mkfs_build_tree(struct erofs_inode *dir, struct list_head *dirs)
{
int ret;
DIR *_dir;
struct dirent *dp;
struct erofs_dentry *d;
unsigned int nr_subdirs, i_nlink;
...
// 如果是文件
if (!S_ISDIR(dir->i_mode)) {
if (S_ISLNK(dir->i_mode)) {
char *const symlink = malloc(dir->i_size);
if (!symlink)
return -ENOMEM;
ret = readlink(dir->i_srcpath, symlink, dir->i_size);
if (ret < 0) {
free(symlink);
return -errno;
}
ret = erofs_write_file_from_buffer(dir, symlink);
free(symlink);
} else if (dir->i_size) {
int fd = open(dir->i_srcpath, O_RDONLY | O_BINARY);
if (fd < 0)
return -errno;
// **写入镜像**
ret = erofs_write_file(dir, fd, 0);
close(fd);
} else {
ret = 0;
}
if (ret)
return ret;
erofs_prepare_inode_buffer(dir);
erofs_write_tail_end(dir);
return 0;
}
// 发现是目录,打开目录并初始化
_dir = opendir(dir->i_srcpath);
if (!_dir) {
erofs_err("failed to opendir at %s: %s",
dir->i_srcpath, erofs_strerror(errno));
return -errno;
}
nr_subdirs = 0;
while (1) {
/*
* set errno to 0 before calling readdir() in order to
* distinguish end of stream and from an error.
*/
errno = 0;
dp = readdir(_dir);
if (!dp)
break;
if (is_dot_dotdot(dp->d_name))
continue;
/* skip if it's a exclude file */
if (erofs_is_exclude_path(dir->i_srcpath, dp->d_name))
continue;
d = erofs_d_alloc(dir, dp->d_name);
if (IS_ERR(d)) {
ret = PTR_ERR(d);
goto err_closedir;
}
nr_subdirs++;
}
...
ret = erofs_prepare_dir_file(dir, nr_subdirs);
if (ret)
return ret;
ret = erofs_prepare_inode_buffer(dir);
if (ret)
return ret;
dir->bh->op = &erofs_skip_write_bhops;
if (IS_ROOT(dir))
erofs_fixup_meta_blkaddr(dir);
// 遍历每个目录项,为每个目录项创建inode
i_nlink = 0;
list_for_each_entry(d, &dir->i_subdirs, d_child) {
char buf[PATH_MAX];
unsigned char ftype;
struct erofs_inode *inode;
if (is_dot_dotdot(d->name)) {
++i_nlink;
continue;
}
...
// 获得目录的inode
inode = erofs_iget_from_path(buf, true);
/* a hardlink to the existed inode */
if (inode->i_parent) {
++inode->i_nlink;
} else {
inode->i_parent = dir;
erofs_igrab(inode);
list_add_tail(&inode->i_subdirs, dirs);
}
// 更新目录项信息
ftype = erofs_mode_to_ftype(inode->i_mode);
i_nlink += (ftype == EROFS_FT_DIR);
d->inode = inode;
d->type = ftype;
erofs_info("file %s/%s dumped (type %u)",
dir->i_srcpath, d->name, d->type);
}
...
return 0;
err_closedir:
closedir(_dir);
return ret;
}4.5 生成镜像文件
在 erofs_mkfs_build_tree 中,遍历到文件就会写入镜像。写入时调用函数 erofs_write_file,这个函数也会判断两种情况:
- 需要压缩,调用压缩函数
erofs_write_compressed_file写入 - 不需要压缩,直接写入
int erofs_write_file(struct erofs_inode *inode, int fd, u64 fpos)
{
int ret;
// 需要压缩
if (cfg.c_compr_alg[0] && erofs_file_is_compressible(inode)) {
ret = erofs_write_compressed_file(inode, fd);
if (!ret || ret != -ENOSPC)
return ret;
ret = lseek(fd, fpos, SEEK_SET);
if (ret < 0)
return -errno;
}
// 不需要压缩
/* fallback to all data uncompressed */
return write_uncompressed_file_from_fd(inode, fd);
}不压缩写入并不重要,我们主要看压缩的逻辑:
int erofs_write_compressed_file(struct erofs_inode *inode, int fd)
{
...
blkaddr = erofs_mapbh(bh->block); /* start_blkaddr */
// 初始化压缩的上下文
ctx.inode = inode;
ctx.pclustersize = z_erofs_get_max_pclustersize(inode);
ctx.blkaddr = blkaddr;
ctx.metacur = compressmeta + Z_EROFS_LEGACY_MAP_HEADER_SIZE;
ctx.head = ctx.tail = 0;
ctx.clusterofs = 0;
ctx.e.length = 0;
ctx.remaining = inode->i_size - inode->fragment_size;
ctx.fix_dedupedfrag = false;
ctx.fragemitted = false;
if (cfg.c_all_fragments && !erofs_is_packed_inode(inode) &&
!inode->fragment_size) {
ret = z_erofs_pack_file_from_fd(inode, fd, ctx.tof_chksum);
if (ret)
goto err_free_idata;
} else {
// 把inode对应文件的数据读到ctx的队列中
while (ctx.remaining) {
const u64 rx = min_t(u64, ctx.remaining,
sizeof(ctx.queue) - ctx.tail);
ret = read(fd, ctx.queue + ctx.tail, rx);
if (ret != rx) {
ret = -errno;
goto err_bdrop;
}
ctx.remaining -= rx;
ctx.tail += rx;
// 压缩文件内容
ret = vle_compress_one(&ctx);
if (ret)
goto err_free_idata;
}
}
DBG_BUGON(ctx.head != ctx.tail);
/* fall back to no compression mode */
...
}
static int vle_compress_one(struct z_erofs_vle_compress_ctx *ctx)
{
// 初始化和配置:存放压缩后的数据
static char dstbuf[EROFS_CONFIG_COMPR_MAX_SZ + EROFS_MAX_BLOCK_SIZE];
struct erofs_inode *inode = ctx->inode;
struct erofs_sb_info *sbi = inode->sbi;
char *const dst = dstbuf + erofs_blksiz(sbi);
struct erofs_compress *const h = &ctx->ccfg->handle;
unsigned int len = ctx->tail - ctx->head;
bool is_packed_inode = erofs_is_packed_inode(inode);
bool final = !ctx->remaining;
int ret;
while (len) {
bool may_packing = (cfg.c_fragments && final &&
!is_packed_inode);
bool may_inline = (cfg.c_ztailpacking && final &&
!may_packing);
bool fix_dedupedfrag = ctx->fix_dedupedfrag;
// 去重
if (z_erofs_compress_dedupe(ctx, &len) && !final)
break;
// 如果文件很小,则考虑不同的策略
if (len <= ctx->pclustersize) {
if (!final || !len)
break;
// 尾部数据打包优化
if (may_packing) {
if (inode->fragment_size && !fix_dedupedfrag) {
ctx->pclustersize =
roundup(len, erofs_blksiz(sbi));
goto fix_dedupedfrag;
}
ctx->e.length = len;
goto frag_packing;
}
// 不内联,直接不压缩写入
if (!may_inline && len <= erofs_blksiz(sbi))
goto nocompression;
}
ctx->e.length = min(len,
cfg.c_max_decompressed_extent_bytes);
// 调用压缩算法压缩数据,存入dst数组
ret = erofs_compress_destsize(h, ctx->queue + ctx->head,
&ctx->e.length, dst, ctx->pclustersize,
!(final && len == ctx->e.length));
if (ret <= 0) {
...
} else if (may_packing && len == ctx->e.length &&
// 尾部数据打包
} else if (may_inline && len == ctx->e.length &&
ret < erofs_blksiz(sbi)) {
// inline数据存到inode里
} else {
// 压缩成功,写入压缩的数据
ret = blk_write(sbi, dst - padding, ctx->blkaddr,
ctx->e.compressedblks);
}
...
}
return 0;
fix_dedupedfrag:
DBG_BUGON(!inode->fragment_size);
ctx->remaining += inode->fragment_size;
ctx->e.length = 0;
ctx->fix_dedupedfrag = true;
return 0;
}
static inline int blk_write(struct erofs_sb_info *sbi, const void *buf,
erofs_blk_t blkaddr, u32 nblocks)
{
return dev_write(sbi, buf, erofs_pos(sbi, blkaddr),
erofs_pos(sbi, nblocks));
}
int dev_write(struct erofs_sb_info *sbi, const void *buf, u64 offset, size_t len)
{
int ret;
// syscall,写入文件
ret = pwrite64(sbi->devfd, buf, len, (off64_t)offset);
return 0;
}完整的流程大致如下:
erofs_mkfs_build_tree
--- erofs_write_file
--- erofs_write_compressed_file
--- vle_compress_one
--- erofs_compress_destsize
--- blk_write最后,镜像的布局如下图: